Accurate local time setting - Learn everything about the atomic clock
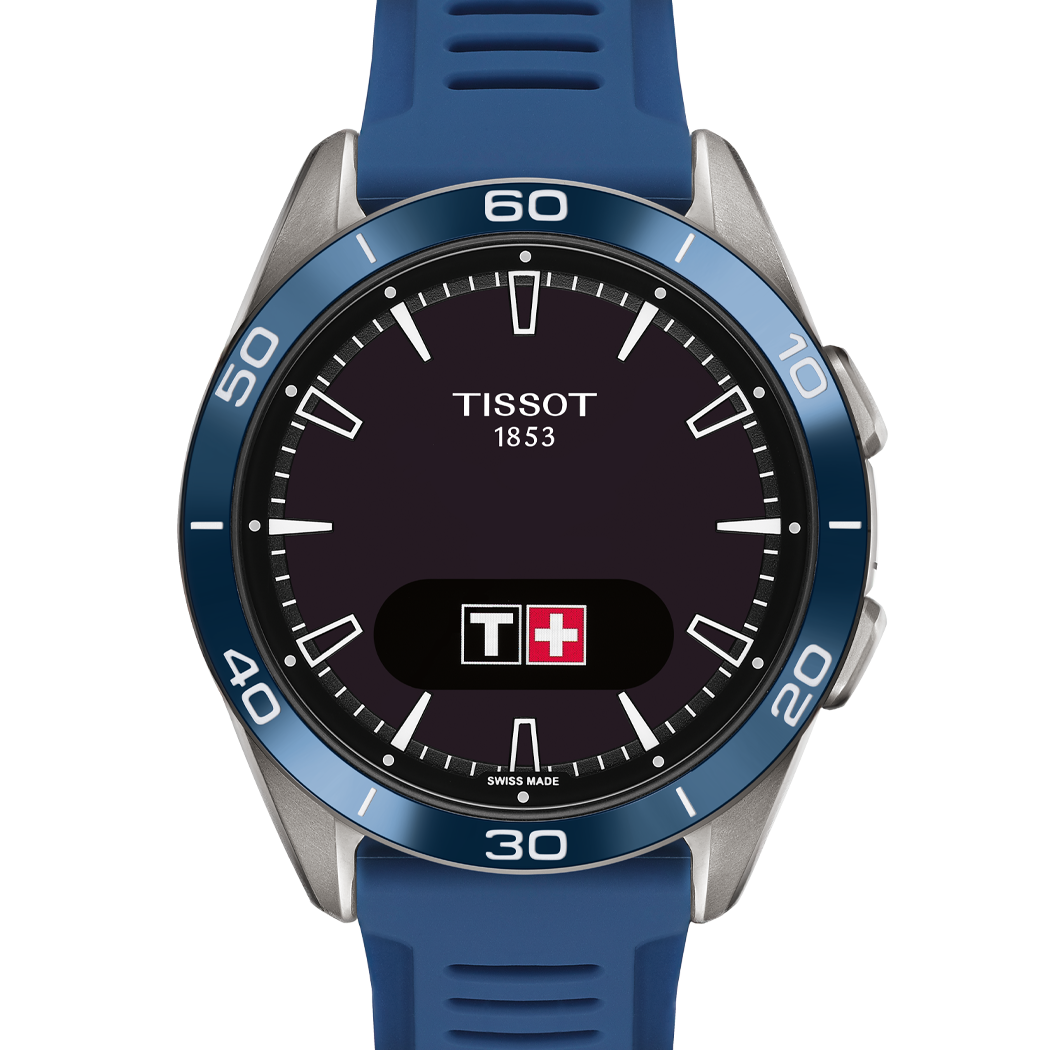


T-Touch Connect Sport Smartwatch
Questions & answers about the atomic clock
What is an atomic clock?
Atomic clocks, developed in the 1950s, measure time with extremely high accuracy, far greater than that of conventional clocks and watches. They define a second with stable accuracy over millions of years. With an atomic clock, you can find out the exact local time setting.
How does an atomic clock work?
An atomic clock uses the vibrations of atoms, such as caesium atoms, to measure time accurately. When caesium atoms change their energy state, they oscillate and emit a very regular frequency, similar to a natural ‘beat’. The clock sends out waves to vibrate these atoms and adjusts the frequency of the waves until it corresponds exactly to the oscillations of the atom. By counting these vibrations (exactly 9,192,631,770 times for one second), the clock can keep time in an incredibly stable way, much more so than ordinary clocks.
How accurate is an atomic clock?
Atomic clocks achieve extraordinary accuracy, with an error of around one second in 30 million years. The Swiss atomic clock in real time is an excellent example of this accuracy and can be used online to display the exact time.
Why are atomic clocks so accurate?
The oscillations of atoms, particularly caesium, are incredibly regular, much more so than those of quartz crystals. Disturbances are minimised because atoms are insensitive to external changes, such as temperature or pressure. In addition, modern atomic clocks use laser cooling techniques and magnetic traps to slow down the atoms and reduce measurement errors.
What is the purpose of an atomic clock?
Modern technology requires extreme precision to synchronise GPS satellites, enabling precise geolocation, and to support telecommunications networks, guaranteeing time consistency for the Internet and banking transactions. Atomic clocks also serve as a reference for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), ensuring precise global time synchronisation.
What is the difference between an atomic watch and a standard watch?
Atomic watches differ considerably from automatic and quartz watches in terms of precision and technology. They are based on the vibrations of atoms such as caesium and offer exceptional precision, drifting by just one second over several million years. Automatic watches, on the other hand, which rely on wrist movement to wind a spring, are less accurate and can drift by several seconds a day. Quartz watches, on the other hand, use the vibration of a quartz crystal to measure time, offering greater accuracy than automatic watches, but cannot match the extreme precision of atomic clocks, which generally drift by a few seconds a month. So, while automatic and quartz watches are suitable for everyday use, atomic clocks are reserved for applications requiring ultra-precise synchronisation.
Where is the atomic clock in Switzerland?
Switzerland's main atomic clock is located at the Federal Laboratory of Metrology (METAS) near Bern. This laboratory is responsible for the country's official time and works with other international institutes to help calculate international atomic time, thus guaranteeing precise synchronisation on a global scale. The exact Swiss time can be consulted online in real time via our atomic clock.
Where are atomic clocks located around the world?
Atomic clocks are found all over the world, mainly in metrology laboratories, universities and government facilities. In addition, many atomic clocks are integrated into navigation satellites, such as those used by GPS, ensuring precise synchronisation for a variety of applications around the world.
How are atomic clocks used in GPS and communications?
Atomic clocks play a crucial role in the GPS system, providing precise atomic time for positioning. They synchronise satellite signals, ensuring reliable geolocation. In telecommunications, they guarantee time synchronisation for data transfer, essential for the smooth operation of the Internet and banking transactions.
Is it possible to buy an atomic clock for personal use?
It is possible to buy an atomic clock, but it costs several thousand francs. An alternative are GPS watches synchronised to atomic time. This allows you to measure time very accurately, regardless of where you are. Our GPS watches are synchronised with GPS satellites equipped with atomic clocks.
Radio-controlled watches are also set to atomic time. Accuracy depends on the quality of reception and the frequency of synchronisation. As a general rule, radio-controlled watches synchronise once a day, which can result in minor discrepancies between synchronisations. Discover our selection of radio-controlled watches online.











